Treatment Advances & Prevention Research
Global Liver Institute brings you key updates in liver cancer research and treatment. We highlight the final results from a Phase II combination therapy trial, along with encouraging data on the integration of immunotherapy and targeted therapies with TACE for patients with intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We also explore emerging research focused on underlying liver conditions that may contribute to cancer risk. Our webinar on liver disease prevention through nutrition—featuring expert insights and patient stories—is now available to watch on GLI’s YouTube channel. Be sure to also explore the upcoming webinars dedicated to supporting the liver cancer patient community.
Missed Our Liver Cancer Lessons Webinar? Watch the Recording!
In our recent webinar, Dr. Jennifer Lai, and patient advocates Karen Hoyt and Susan Horava, discussed Liver Disease Prevention Through Nutrition. Check out the recording to learn how nutrition impacts liver disease, discover practical tips to support a healthy liver, and hear answers to some of the most common nutrition-related questions.
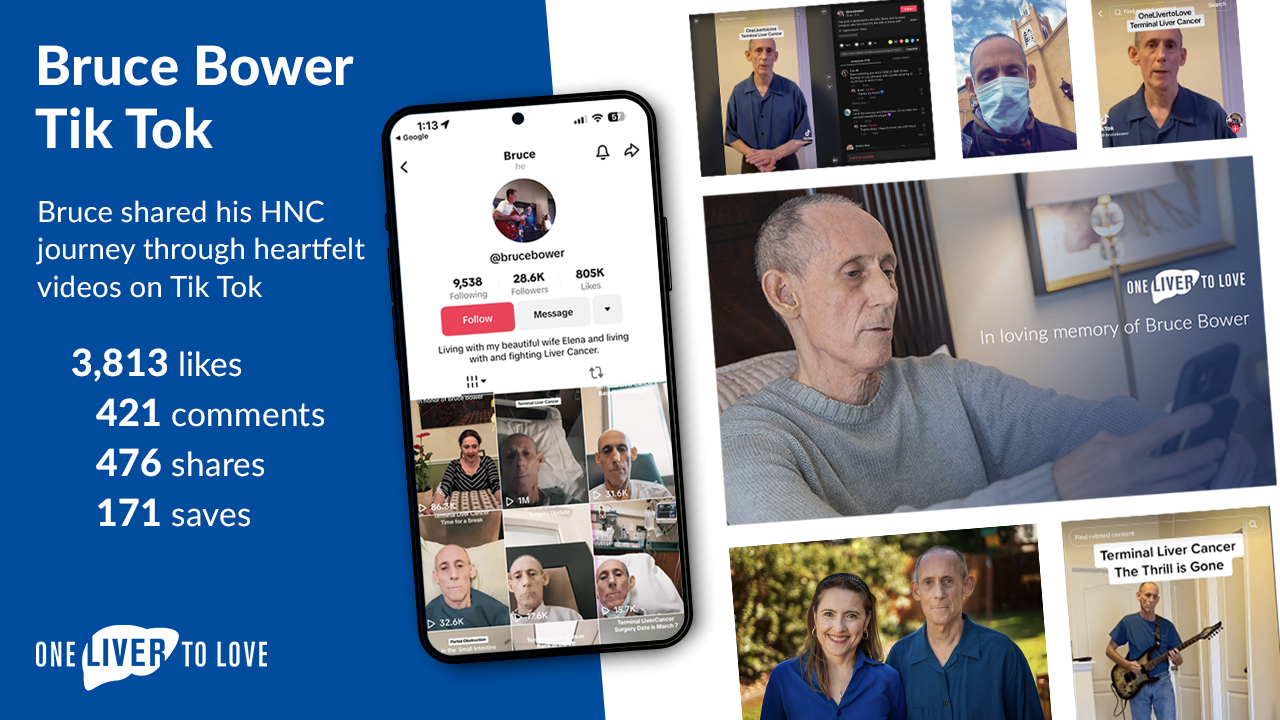
One Liver to Love Campaign wins the MUSE Creative Awards!
We’re thrilled to share that the One Liver to Love campaign has won a Gold Award in the MUSE Creative Awards for its engaging TikTok video series featuring Bruce Bower! This recognition in the Social Media – Healthcare & Pharma category celebrates the campaign’s creative impact in raising liver cancer awareness through innovative storytelling and digital outreach.
Combining TACE with Systemic Therapies Improves Outcomes in Intermediate-Stage HCC
Two clinical trials have shown that adding systemic therapies to transarterial chemoembolization (TACE)—a standard treatment that delivers chemotherapy directly to liver tumors—can benefit patients with intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In the LEAP-012 trial, TACE was combined with pembrolizumab (Keytruda) and lenvatinib (Lenvima), while the EMERALD-1 trial combined TACE with durvalumab (Imfinzi) and bevacizumab. Both studies found that patients who received these combination treatments lived significantly longer without their cancer progressing compared to those who received TACE alone, with progression-free survival extended to about 15 months versus 8 to 10 months. These results suggest that combining TACE with immunotherapy and targeted drugs could offer a more effective treatment option and potentially become a new standard of care for patients with intermediate-stage HCC.
Final Phase 2 Data Show Promise for Casdozokitug Combination in Advanced Liver Cancer
At the January 2025 ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium, researchers presented promising results from a Phase 2 clinical trial for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who had not received prior treatment. The study tested a new drug, casdozokitug, which targets the IL-27 protein involved in cancer growth, in combination with atezolizumab, an immunotherapy, and bevacizumab, which blocks the formation of blood vessels that feed tumors. The results showed that 38% of patients experienced tumor shrinkage, and 17.2% had no detectable cancer after treatment. These responses were observed regardless of the underlying cause of liver cancer, including hepatitis or other factors. The treatment combination also showed manageable side effects. A larger trial is now underway to further explore casdozokitug with other immunotherapy and anti-angiogenic drugs.
New Drug Candidate Shows Promise Against MASLD and Liver Cancer in Preclinical Study
Researchers are investigating new treatments for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), a condition linked to obesity and diabetes that increases the risk of liver cancer. A recent study published in Nature Aging highlighted a promising drug designed to eliminate senescent—or “zombie”—cells in the liver, which contribute to liver damage and cancer development in MASLD. In lab and animal studies, the drug successfully reduced liver fat, fibrosis, and tumor growth without causing the toxic side effects seen in previous senescent cell-targeting drugs. Although still in the early preclinical stage, this research points to a potential new approach for preventing liver cancer by treating the root causes of MASLD.
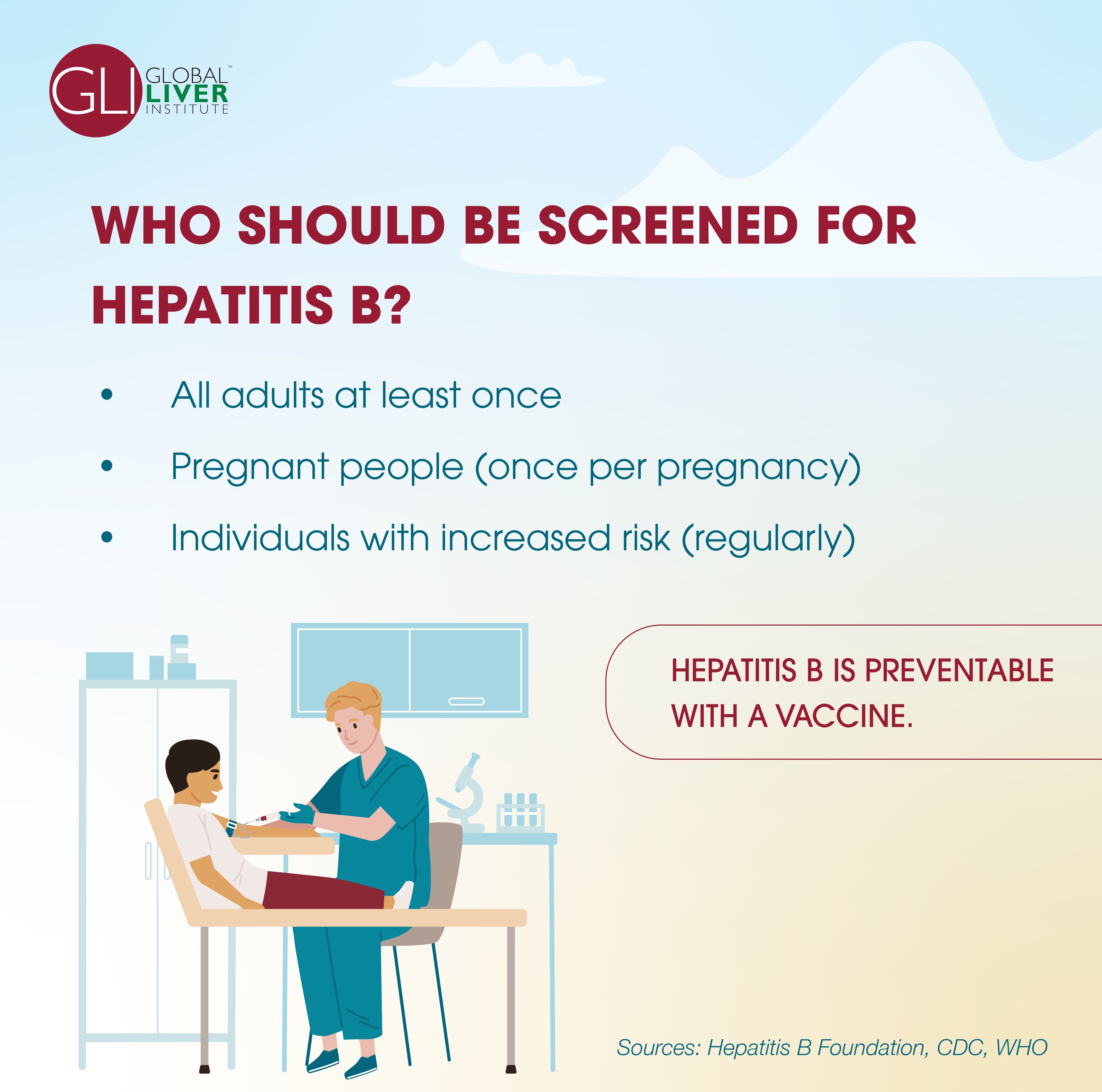
Proactive Protection of the Liver Health of Asian Americans
Did you know that everyone should be screened for Hepatitis B? This infection can slowly and quietly cause liver damage over the years, eventually leading to liver cancer in many cases. Certain communities, such as Asian Americans and Asian-American immigrants, have a higher risk of hepatitis B. Fortunately, hepatitis B infection is preventable with a vaccine and its progression can be managed with ongoing treatment, if needed after screening. Learn more about this in our recent blog post.
Upcoming Events:
- May 7, 2025: Webinar: Caring for your Wellbeing: Strategies for Taking Care of your Emotional Health (Spanish)
- May 7- 10, 2025: EASL Congress, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
- May 17, 2025: Triage Health Online Conference
- May 22, 2025: Together for Better Liver Health: Strengthening Public Health Responses to Metabolic Disease; a GLI, EASL, and AASLD policy event on the sidelines of the WHA78, Geneva, Switzerland
- May 29, 2025: Webinar: Hepatitis C in Latin America and North America (Spanish)
- June 12, 2025: Global Fatty Liver Day
- July 22, 2025: Webinar: Accessing & Paying for Clinical Trials
For more information about the Liver Cancers Council or to learn more about joining, please visit https://globalliver.org/liver-cancers-council/ or email cancer@globalliver.org